要点
大脑是一个复杂的,互联网络;大脑的连接拓扑因此从根本上形状出现,表达和大脑疾病的进展。
理解大脑的疾病需要知识的大脑网络响应-自适应或适应不良的病理微扰。
迅速发展的领域——提供新的工具来描述和建模这些反应。
大脑疾病的效果严重依赖于拓扑中心和简并受影响的区域;病理学的中部地区加剧了不适应的反应,而简并促进适应性反应
文摘
病理扰动的大脑很少局限于一个单一的轨迹;相反,他们常常通过轴突路径影响其他地区的传播。这种疾病传播模式受到极其复杂,然而高度有组织的,潜在的神经结构的拓扑结构;所谓的连接体。因此,网络组织从根本上影响大脑疾病和connectomic方法基于网络科学理解神经病理学是不可或缺的。在这里,我们考虑脑网络拓扑形状神经反应破坏,强调关键不适应的过程(如双价染色体分离,transneuronal变性和去分化),和资源(包括简并和储备)和过程(如补偿),使适应。然后我们展示网络拓扑的知识使我们不仅描述病理过程,而且生成预测模型的扩散和功能性脑疾病的后果。
这是一个预览的订阅内容,通过访问你的机构
相关的文章
开放获取文章引用这篇文章。
非传统的大脑认知网络参与insulo-Sylvian神经胶质瘤:使用Quicktome病例系列研究和临床经验
中国神经外科杂志开放获取2023年5月26日
白质的异常的拓扑网络甲基苯丙胺依赖患者在基于支持向量机的分类及其应用
科学报告开放获取2023年4月28日
试再现性变化多,纵向的大脑网络
科学报告开放获取2023年4月24日
访问选项
订阅本杂志
收到12印刷问题和网络访问
每年189.00美元
只有15.75美元的问题
本文租或购买
本文得到只要你需要它
39.95美元
价格可能受当地税收计算在结帐

引用
西格尔,r E。盖伦在受影响的部分(Karger出版社,1976)。
手指,S。,Koehler, P. J. & Jagella, C. The von Monakow concept of diaschisis: origins and perspectives.拱门。神经。61年,283 - 288 (2004)。
克勒,p . j . Brown-Sequard和脑定位了他的想法在失语症。j .嘘。>。526-33 (1996)。
Monakow,冯,c大脑和行为Vol.I:情绪、状态和思想(ed Pribram, k . h) 27-36(企鹅出版社,1969)。
捐助,d . m . &男爵,j . c双价染色体分离。中风17,817 - 830 (1986)。
韦尼克,aphasie一些新的研究。Fortschr。地中海。824 - 830 (1885)。
卡塔尼亚、m & ffytche d.h断开综合症的起落。大脑128年,2224 - 2239 (2005)。本文提供了一个彻底的作用连接神经系统疾病的变化。
Geschwind:分开综合症在动物和人。我一部分。大脑88年,237 - 294 (1965)。
Geschwind:分开综合症在动物和人。第二部分。大脑88年,585 - 644 (1965)。
Mesulam, m . m .大规模神经认知网络和分布式处理的关注,语言,和记忆。安。神经。28,597 - 613 (1990)。
达马西奥,a . r .寿命multiregional retroactivation:系统性提议的神经基质召回和认可。认知33,25 - 62 (1989)。
布洛卡,p . Perte de la假释:ramollissement chronique等破坏partielle杜叶anterieur偏转du cerveau。公告Soc。Anthropolgie2,235 - 238(法国)(1861)。
哈洛,j . m .通过一个铁棒头。波士顿医疗。Surg. J。39,389 - 393 (1848)。
斯科维尔,w . b . &米尔纳,b侧海马损伤后近期记忆丧失。j .神经Neurosurg。精神病学20.乳(1957)。
图像,大肠&斯波恩,o .复杂的大脑网络:图结构和功能系统的理论分析。自然启>。10,186 - 198 (2009)。本文介绍的应用图论和网络科学神经科学数据。
托诺尼,G。,斯波恩,O。&Edelman, G. M. A measure for brain complexity: relating functional segregation and integration in the nervous system.Proc。《科学。美国91年,5033 - 5037 (1994)。
Breakspear, m &斯塔姆,c . j .神经系统的动力学与多尺度结构。菲尔。反式。r . Soc。Lond。B360年,1051 - 1074 (2005)。
Buldyrev, s V。Parshani, R。,保罗,G。,Stanley, H. E. & Havlin, S. Catastrophic cascade of failures in interdependent networks.自然464年,1025 - 1028 (2011)。
可,a . c . et al .频繁发作与网络相关联的灰质萎缩在颞叶癫痫有或没有海马硬化。《公共科学图书馆•综合》9e85843 (2014)。
Rehme, a . k . & Grefkes c .脑卒中后网络障碍:证据从成像进行连通性分析人类活动和休息的大脑状态。j .杂志。591年17-31 (2012)。
Tabrizi, s . j . et al .生物和亨廷顿氏病的临床表现纵向TRACK-HD研究:横断面分析基线数据。柳叶刀神经。8,791 - 801 (2009)。
Goedert, M。,Spillantini, M. G., Del Tredici, K. & Braak, H. 100 years of Lewy pathology.自然启神经。924里面(2012)。
斯波恩,o .人类连接体:人类大脑的结构描述。公共科学图书馆第一版。医学杂志。1e42 (2005)。介绍了连接体的概念,并概述了战略连接体映射。
Bohland, j . w . et al .提案的协调努力的决心brainwide神经解剖学的连接在介观尺度的生物模型。公共科学图书馆Comp。杂志。5e1000334 (2009)。
坎德尔,e R。马克莱姆,H。,Matthews, P. M., Yuste, R. & Koch, C. Neuroscience thinks big (and collaboratively).自然启>。14,659 - 664 (2013)。
范·埃森特区& Ugurbil k的未来人类的连接体。科学杂志62年,1299 - 1310 (2012)。
哦,s . w . et al .中尺度老鼠大脑的连接体。自然508年,207 - 214 (2014)。
蒋介石,a . s . et al . brain-wide连接网络的三维重建果蝇在单细胞的决议。咕咕叫。医学杂志。211 - 11 (2011)。
马尔可夫:t . et al .加权和导演interareal连接矩阵猕猴大脑皮层。Cereb。皮质2417-36 (2013)。
白色,j·G。,Southgate, E., Thomson, J. N. & Brenner, S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode秀丽隐杆线虫。菲尔。反式。r . Soc。Lond。B314年1 - 340 (1986)。
Herculano-Houzel,美国人类的大脑在数字:一个线性比例增大的灵长类动物大脑。前面。嗡嗡声。>。931 (2009)。
Pakkenberg, b . et al .衰老和人类大脑皮层。Exp Gerontol。38,95 - 99 (2003)。
Kasthuri: &李奇曼j·w·Neurocartography。神经精神药理学35,342 - 343 (2010)。
图像,大肠&斯波恩,o .大脑网络的经济组织。自然启>。13,336 - 349 (2012)。
克罗斯利:a . et al。人类的中心连接体通常涉及脑部疾病的解剖。大脑137年,2382 - 2395 (2014)。本研究使用荟萃分析的分布形态测量学研究各种脑部疾病显示病变往往发生在网络中心的大脑区域。
野村证券(Nomura) e . M。,Gratton, C. & Visser, R. M. Double dissociation of two cognitive control networks in patients with focal brain lesions.Proc。《科学。美国107年,12017 - 12022 (2010)。
黄金,l . & Lauritzen m .神经失活解释小脑血流减少响应局灶性脑缺血或抑制皮层功能。Proc。《科学。美国99年,7699 - 7704 (2002)。
亲爱的,c . j . &斯波恩,o .动力损伤皮层网络的后果。嗡嗡声。攻读硕士学位的大脑。29日,802 - 809 (2008)。
Alstott, J。,Breakspear, M., Hagmann, P., Cammoun, L. & Sporns, O. Modeling the impact of lesions in the human brain.公共科学图书馆Comp。杂志。5e1000408 (2009)。本研究使用大脑的神经质量模型动力学,模拟经验结构连接网络模型的功能连通性变化引起的不同类型的结构损伤人的连接体。
卡雷拉,大肠&托诺尼g双价染色体分离:过去,现在,未来。大脑137年,2408 - 2422 (2014)。
Corbetta, M。,Kincade, M. J., Lewis, C., Snyder, A. Z. & Sapir, A. Neural basis and recovery of spatial attention deficits in spatial neglect.自然>。8,1603 - 1610 (2005)。
他,b . j . et al .分解的功能连通性frontoparietal网络构成与空间忽视行为缺陷。神经元53,905 - 918 (2007)。
范·米尔·m·p·a . et al。实验中风后感觉运动功能的恢复与重建的静息状态的两半球间的功能连通性。j . >。30.,3964 - 3972 (2010)。
范·米尔·m·p·a . et al。双边神经元网络重组和功能恢复的程度与中风严重性。j . >。32,4495 - 4507 (2012)。
价格,c·J。,Warburton, E. A., Moore, C. J., Frackowiak, R. S. & Friston, K. J. Dynamic diaschisis: anatomically remote and context-sensitive human brain lesions.j . Cogn。>。13,419 - 429 (2001)。
Napieralski, j . A。,Butler, A. K. & Chesselet, M. F. Anatomical and functional evidence for lesion-specific sprouting of corticostriatal input in the adult rat.j . Comp。神经。373年,484 - 497 (1996)。
卡特,a . r . et al .休息两半球间的功能性磁共振成像的连通性预测中风后的性能。安。神经。67年,365 - 375 (2010)。
考恩,w . M。现代神经解剖学的研究方法(Springer, 1970)。本文提供了一个全面的概述各类transneuronal变性。
戴勒,T。,Del Turco, D., Rappert, A. & Bechmann, I. in齿状回:一个全面的指南,结构,功能和临床意义(ed Scharfman, h) 501 - 528(爱思唯尔,2007)。
DeGiorgio,洛杉矶。Dibinis C。,Milner, T. A., Saji, M. & Volpe, B. T. Histological and temporal characteristics of nigral transneuronal degeneration after striatal injury.大脑Res。795年1 - 9 (1998)。
休博尔,d·h·&维塞尔,t . n的易感性在小猫单边闭目的生理效应。j .杂志。206年,419 - 436 (1970)。
比蒂,r . M。,Sadun, A. A. & Smith, L. Direct demonstration of transsynaptic degeneration in the human visual system: a comparison of retrograde and anterograde changes.j .神经。45,143 - 146 (1982)。
你,Y。,Gupta, V. K., Graham, S. L. & Klistorner, A. Anterograde degeneration along the visual pathway after optic nerve injury.《公共科学图书馆•综合》7e52061 (2012)。
哈尔滨市,M。,Boire, D., Théoret, H. & Ptito, M. Transneuronal degeneration of retinal ganglion cells in early hemispherectomized monkeys.Neuroreport10,1447 - 1452 (1999)。
Cowey,。,Stoerig, P. & Williams, C. Variance in transneuronal retrograde ganglion cell degeneration in monkeys after removal of striate cortex: effects of size of the cortical lesion.视觉Res。39,3642 - 3652 (1999)。
Saxena, s &卡罗尼河,p .选择性神经退行性疾病的神经脆弱:从压力阈值退化。神经元71年35-48 (2011)。
Perlson E。、Maday年代。傅,M . M。,Moughamian, A. J. & Holzbaur, E. L. F. Retrograde axonal transport: pathways to cell death?趋势>。33,335 - 344 (2010)。
迈尔斯:et al . Within-patient通信amyloid-β和内在的网络连接在阿尔茨海默氏症。大脑137年,2052 - 2064 (2014)。
Klupp、大肠等。在阿尔茨海默氏症、代谢减退在low-amyloid大脑区域可能是病态的功能结果在连接大脑区域。4,371 - 383 (2014)。
周,J。,Gennatas, E. D., Kramer, J. H., Miller, B. L. & Seeley, W. W. Predicting regional neurodegeneration from the healthy brain functional connectome.神经元73年,1216 - 1227 (2012)。
罗斯,d t & it f . f .丘脑逆行变性后皮质损伤:一个excitotoxic过程?神经科学35,525 - 550 (1990)。
Vucic, S。,Ziemann, U., Eisen, A., Hallett, M. & Kiernan, M. C. Transcranial magnetic stimulation and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: pathophysiological insights.j .神经。Neurosurg。精神病学84年,1161 - 1170 (2013)。
是E。,Veldink, J. H., van den Berg, L. H. & van den Heuvel, M. P. Structural brain network imaging shows expanding disconnection of the motor system in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.嗡嗡声。攻读硕士学位的大脑。35,1351 - 1361 (2013)。
Bartzokis g·阿尔茨海默病,稳态响应与年龄相关的髓磷脂崩溃。一般人。老化32,1341 - 1371 (2011)。
Hirokawa, N。,Niwa, S. & Tanaka, Y. Molecular motors in neurons: transport mechanisms and roles in brain function, development, and disease.神经元68年,610 - 638 (2010)。
中殿,K.-A。长轴突髓鞘形成的营养支持。自然启>。11,275 - 283 (2010)。
霜,b &钻石,麻省理工学院Prion-like机制在神经退行性疾病。自然启>。11,155 - 159 (2009)。
巴克纳,r . l . et al .分子结构,阿尔茨海默氏症和功能描述:默认活动之间的关系的证据,淀粉样蛋白,和记忆。j . >。25,7709 - 7717 (2005)。
斯利,W W。,Crawford, R. K., Zhou, J., Miller, B. L. & Greicius, M. D. Neurodegenerative diseases target large-scale human brain networks.神经元62年42-52 (2009)。本研究报告证明灰质萎缩一系列神经退行性疾病可能发生在功能和结构上连接神经系统。
李,s . C。,Lindenberger, U. & Sikström, S. Aging cognition: from neuromodulation to representation.认知科学趋势。5,479 - 486 (2001)。
王侯,m . n .针对性前额叶功能随着年龄的变化:宠物和功能磁共振成像研究的审查工作和情景记忆。大脑128年,1964 - 1983 (2005)。
Rehme, a K。,Eickhoff, S. B., Wang, L. E., Fink, G. R. & Grefkes, C. Dynamic causal modeling of cortical activity from the acute to the chronic stage after stroke.科学杂志55,1147 - 1158 (2011)。
Grefkes, c . et al .调制皮层连接在中风患者用fMRI rTMS评估和动态因果模型。科学杂志50,233 - 242 (2010)。
Fornito, a &图像,e . t .协调异常的精神分裂症的脑结构和功能网络。现在的当今。一般人。30 c, 44-50 (2014)。
Minzenberg, m . J。Laird, a。R。泰伦,S。,Carter, C. S. & Glahn, D. C. Meta-analysis of 41 functional neuroimaging studies of executive function in schizophrenia.拱门。他精神病学66年,811 - 822 (2009)。
冬天,g . &温伯格d r基因,多巴胺和皮质信噪比在精神分裂症。趋势>。27,683 - 690 (2004)。
Fornito,。,Zalesky,。,Pantelis, C. & Bullmore, E. T. Schizophrenia, neuroimaging and connectomics.科学杂志62年,2296 - 2314 (2012)。
温伯格,d . r .影响大脑正常发育的精神分裂症的发病机理。拱门。他精神病学44,660 - 669 (1987)。
马德尔,大肠& Goaillard人类。可变性,补偿和体内平衡在神经元和网络功能。自然启>。7,563 - 574 (2006)。
卒中后阿富汗二月,d .动态语言的重组。大脑129年,1371 - 1384 (2006)。
Bestmann, s . et al。卒中后contralesional背侧前运动皮层的作用与并发TMS-fMRI研究。j . >。30.,11926 - 11937 (2010)。
riecke, a . et al .的角色半球卒中后运动恢复的影响。嗡嗡声。攻读硕士学位的大脑。31日,1017 - 1029 (2010)。
Rehme, a K。,Eickhoff, S. B., Rottschy, C., Fink, G. R. & Grefkes, C. Activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of motor-related neural activity after stroke.科学杂志59,2771 - 2782 (2012)。
奥谢,J。,Johansen-Berg, H., Trief, D., Gobel, S. & Rushworth, M. F. Functionally specific reorganization in human premotor cortex.神经元54,479 - 490 (2007)。在这项研究中,作者使用经颅磁刺激和功能磁共振成像显示,电机性能是抑制TMS的左背侧前运动皮层后,保存,这种保护是由于补充招聘侧(右)前运动皮层。
·约翰森伯格h . et al .侧前运动皮层的作用在卒中后运动。Proc。《科学。美国99年,14518 - 14523 (2002)。
霜,s . b .重组远程缺血性脑损伤后大脑皮层区域:一个潜在的衬底中风的复苏。j . Neurophysiol。89年,3205 - 3214 (2003)。
沃德:美国卒中后神经的相关汽车复苏:纵向功能磁共振成像研究。大脑126年,2476 - 2496 (2003)。
de Haan W。莫特,K。,van Straaten, E. C. W., Scheltens, P. & Stam, C. J. Activity dependent degeneration explains hub vulnerability in Alzheimer's disease.公共科学图书馆Comp。杂志。8e1002582 (2012)。本文的作者模拟计算模型的依赖性活动退化扩散MRI-derived结构连接网络证明瞬态增加活动之前逐步下降,而中心地区特别容易变性。
斯珀林,r .功能性核磁共振的研究关联编码在正常老化,轻度认知障碍和老年痴呆症。安。纽约私立高中科学。1097年,146 - 155 (2007)。
Poudel, g R。,Egan, G. F. & Churchyard, A. Abnormal synchrony of resting state networks in premanifest and symptomatic Huntington disease: the IMAGE-HD study.j .精神病学>。39,87 - 96 (2014)。
Schoonheim, m . m . &菲利皮主持,m .功能可塑性女士:朋友还是敌人?首页79年,1418 - 1419 (2012)。
Grady, c . l . et al .证据功能神经影像学的补偿性前额网络在阿尔茨海默氏症。j . >。23,986 - 993 (2003)。
科尔布,b & Teskey g . c .年龄、经验、损伤,和大脑的变化。Dev Psychobiol。54,311 - 325 (2010)。
Buchkremer-Ratzmann, i & Witte o . w .扩展大脑抑制解除后小photothrombotic病变大鼠额叶皮质。Neuroreport8,519 - 522 (1997)。
Butefisch, c . m .远程卒中后皮质兴奋性的变化。大脑126年,470 - 481 (2003)。
Liepert, J。,Hamzei, F. & Weiller, C. Motor cortex disinhibition of the unaffected hemisphere after acute stroke.肌肉神经23,1761 - 1763 (2000)。
Marik, s。,Yamahachi, H., Meyer zum Alten Borgloh, S. & Gilbert, C. D. Large-scale axonal reorganization of inhibitory neurons following retinal lesions.j . >。34,1625 - 1632 (2014)。
冈萨雷斯,c . l . r . &科尔布,b .比较不同模型的中风大脑行为和形态。欧元。j . >。18,1950 - 1962 (2003)。
琼斯,t . a . & Schallert t Use-dependent后皮层锥体神经元损伤的增长。j . >。14,2140 - 2152 (1994)。
卡迈克尔,s t & Chesselet m . f .同步神经元活动是一种信号,让轴突皮质病变在成人后发芽。j . >。22,6062 - 6070 (2002)。
Schaechter, j . D。摩尔,c。I。,Connell, B. D., Rosen, B. R. & Dijkhuizen, R. M. Structural and functional plasticity in the somatosensory cortex of chronic stroke patients.大脑129年,2722 - 2733 (2006)。
托诺尼,G。,斯波恩,O。&Edelman, G. M. Measures of degeneracy and redundancy in biological networks.Proc。《科学。美国96年,3257 - 3262 (1999)。
北野,h .生物鲁棒性。自然启麝猫。5,826 - 837 (2004)。
Noppeney U。,Friston, k . J。&价格,c·J。Degenerate neuronal systems sustaining cognitive functions.j·阿娜特。205年,433 - 442 (2004)。本文综述不同形式的神经退化和他们如何支持脑损伤后认知。
Seghier, m . L。李,h·L。,Schofield, T., Ellis, C. L. & Price, C. J. Inter-subject variability in the use of two different neuronal networks for reading aloud familiar words.科学杂志42,1226 - 1236 (2008)。
Friston, k . j . &价格,c . j .模块和大脑映射。认知Neuropsychol。28,241 - 250 (2011)。
Barulli d &斯特恩,y效率、容量、补偿、维护、可塑性:新兴概念认知储备。认知科学趋势。17,502 - 509 (2013)。
Valenzuela, m . J。Breakspear, M。&Sachdev, P. Complex mental activity and the aging brain: molecular, cellular and cortical network mechanisms.大脑的牧师》。56,198 - 213 (2007)。
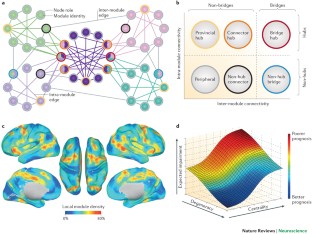
Borgatti, s p中心和网络流量。社交网络2755 - 71 (2005)。
巴斯a . l . &阿尔伯特·r .出现随机网络的扩展。科学286年,509 - 512 (1999)。
Hagmann, p . et al .映射人类整个大脑结构网络扩散磁共振成像。《公共科学图书馆•综合》2e597 (2007)。
艾伯特,R。,Jeong, H. & Barabasi, A. L. Error and attack tolerance of complex networks.自然406年,378 - 382 (2000)。
van den Heuvel, m p &斯波恩,o .峰会组织人类连接体。j . >。31日,15775 - 15786 (2011)。
Zamora-Lopez, g .皮质中心形成一个多种感觉的集成模块的皮质网络的层次结构。弗伦联盟。Neuroinform。194 (2010)。
Harriger, L。,van den Heuvel, m . P。&斯波恩,O。Rich club organization of macaque cerebral cortex and its role in network communication.《公共科学图书馆•综合》7e46497 (2012)。
克罗斯利:A。,Mechelli, A. & Vertes, P. E. Cognitive relevance of the community structure of the human brain functional coactivation network.Proc。《科学。美国110年,11583 - 11588 (2013)。
史密斯,s m . et al。信件在激活期间大脑的功能体系结构和休息。Proc。《科学。美国106年,13040 - 13045 (2009)。
Guimera, r & Nunes Amaral,洛杉矶功能复杂的代谢网络的制图。自然433年,895 - 900 (2005)。
Fornito,。,Harrison, B. J., Zalesky, A. & Simons, J. S. Competitive and cooperative dynamics of large-scale brain functional networks supporting recollection.Proc。《科学。美国109年,12788 - 12793 (2012)。
权力,j . D。,Schlaggar, B. L., Lessov-Schlaggar, C. N. & Petersen, S. E. Evidence for hubs in human functional brain networks.神经元79年,798 - 813 (2013)。
沃伦,d . e . et al .网络措施预测脑损伤后神经心理的结果。Proc。《科学。美国188金宝慱官网下载,14247 - 14252 (2014)。这是第一个示范在人类患者公认的桥中心的大脑损伤导致广泛的神经心理障碍。
Kitsak, M。,Gallos, L. K., Havlin, S., Liljeros, F. & Muchnik, L. Identification of influential spreaders in complex networks.物理性质。6,888 - 893 (2010)。
Palop, J·J。,Chin, J. & Mucke, L. A network dysfunction perspective on neurodegenerative diseases.自然443年,768 - 773 (2006)。
拉吉,一个。,Kuceyeski, A. & Weiner, M. A network diffusion model of disease progression in dementia.神经元73年,1204 - 1215 (2012)。这是第一次证明疾病扩散的一个相对简单的模型,模拟在结构网络体系结构,推导出经验与扩散磁共振成像,可以再现的空间地形萎缩性变化出现在阿尔茨海默病以及额颞叶痴呆。
Buckner, r . l . et al .皮质中心揭示了内在功能连通性:映射,评估稳定,与阿尔茨海默病的关系。j . >。29日,1860 - 1873 (2009)。
van den Heuvel, m . P。卡恩,r S。,Goni, J. & Sporns, O. High-cost, high-capacity backbone for global brain communication.Proc。《科学。美国109年,11372 - 11377 (2012)。
梁,X。邹,Q。,He, Y. & Yang, Y. Coupling of functional connectivity and regional cerebral blood flow reveals a physiological basis for network hubs of the human brain.Proc。《科学。美国110年,1929 - 1934 (2013)。
预,D。,Wang, G. J. & Volkow, N. D. Energetic cost of brain functional connectivity.Proc。《科学。美国110年,13642 - 13647 (2013)。
斯波恩,O。,Honey, C. J. & Kotter, R. Identification and classification of hubs in brain networks.《公共科学图书馆•综合》2e1049 (2007)。
Variano e . a &利普森h .网络动力学和模块化。理论物理。启。92年188701 (2004)。
Brummitt, c, D & D’索萨,r . m .抑制负载在相互依赖的网络的级联。Proc。《科学。美国109年E680-E689 (2012)。
凯撒,M。,Gorner, M. & Hilgetag, C. C. Criticality of spreading dynamics in hierarchical cluster networks without inhibition.新的期刊。9,2 - 13 (2007)。
特里,j . R。,Benjamin, O. & Richardson, M. P. Seizure generation: the role of nodes and networks.Epilepsia53e166-e169 (2012)。
Nepusz, T。,Négyessy, L. & Bazsó, F. Fuzzy communities and the concept of bridgeness in complex networks.物理启E。77年016107 (2008)。
麦金托什,a . r .上下文和催化剂:解决本地化和大脑功能的集成。Neuroinformatics2,175 - 182 (2004)。
吴,k . et al。大脑结构网络的重叠社区结构年轻健康的人。《公共科学图书馆•综合》6e19608 (2011)。
Zalesky a . & Fornito a a DTI-derived cortico-cortical连接。IEEE反式。医疗成像。28,1023 - 1036 (2009)。
亚历山大,d . c . et al。方向不变的指数扩散磁共振成像的轴突直径和密度。科学杂志52,1374 - 1389 (2010)。
Seghier m . l . & Friston k . j .网络发现还大。科学杂志68年,181 - 191 (2013)。
福瑞尔,F。,Aquino, K., Robinson, P. A., Ritter, P. & Breakspear, M. Bistability and non-Gaussian fluctuations in spontaneous cortical activity.j . >。29日,8512 - 8524 (2009)。
Friston, k . J。卡亨,J。,∙B。&Razi, A. A. DCM for resting state fMRI.科学杂志94年,396 - 407 (2014)。
Zalesky,。,Fornito,。,Cocchi, L., Gollo, L. L. & Breakspear, M. Time-resolved resting-state brain networks.Proc。《科学。美国188金宝慱官网下载,10341 - 10346 (2014)。
大卫,o . et al .识别与功能性核磁共振神经司机:一个电生理学的验证。公共科学图书馆杂志。6,2683 - 2697 (2008)。
福瑞尔,F。,Roberts, J. A. & Becker, R. Biophysical mechanisms of multistability in resting-state cortical rhythms.j . >。31日,6353 - 6361 (2011)。
斯蒂芬,k . e . et al。神经系统动力学的动态因果模型:当前状态和未来的扩展。j . Biosci。32,129 - 144 (2007)。
Jirsa诉K。斯波恩,O。,Breakspear, M., Deco, G. & McIntosh, A. R. Towards the virtual brain: network modeling of the intact and the damaged brain.拱门。Italiennes杂志。148年,189 - 205 (2010)。
里特,P。,Schirner, M., McIntosh, A. R. & Jirsa, V. K. The virtual brain integrates computational modeling and multimodal neuroimaging.大脑的连接。3,121 - 145 (2013)。
Fornito,。,Zalesky,。&Breakspear, M. Graph analysis of the human connectome: promise, progress, and pitfalls.科学杂志80年,426 - 444 (2013)。论述了人类神经影像数据的优点和缺陷的分析基于图论。
叶,F.-C。,Verstynen, T. D., Wang, Y., Fernández-Miranda, J. C. & Tseng, W. Y. I. Deterministic diffusion fiber tracking improved by quantitative anisotropy.《公共科学图书馆•综合》8e80713 (2013)。
琼斯·d·K。,Knösche, T. R. & Turner, R. White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: the do's and don'ts of diffusion MRI.科学杂志73年,239 - 254 (2013)。
Friston, k . j .功能神经影像学和有效连接:合成。嗡嗡声。攻读硕士学位的大脑。256 - 78 (1994)。
Fornito,。尹,J。,Zalesky,。,Bullmore, E. T. & Carter, C. S. General and specific functional connectivity disturbances in first-episode schizophrenia during cognitive control performance.医学杂志。精神病学70年,64 - 72 (2011)。
Friston, k . J。,Harrison, L. & Penny, W. Dynamic causal modelling.科学杂志19,1273 - 1302 (2003)。
∙B。,Yetkin, F. Z., Haughton, V. M. & Hyde, J. S. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI.磁铁。地中海研究》。34,537 - 541 (1995)。
福克斯,m . d . & Raichle m . e .自发波动与功能性磁共振成像的大脑活动的观察。自然启>。8,700 - 711 (2007)。
Fornito, a &图像,e . t .自发波动的血液oxygenation-level-dependent信号告诉我们关于精神疾病?咕咕叫。当今。精神病学23,239 - 249 (2010)。
Zalesky,。,Fornito,。&Bullmore, E. T. Network-based statistic: identifying differences in brain networks.科学杂志53,1197 - 1207 (2010)。
Fornito,等。基因影响的人类大脑皮层功能网络的组织。j . >。31日,3261 - 3270 (2011)。
巴,d . s . et al。高效的物理拓扑复杂信息处理网络的嵌入在大脑和计算机电路。公共科学图书馆Comp。杂志。6e1000748 (2010)。
贝露D。,Lambiotte, R., Fornito, A., Ersche, K. D. & Bullmore, E. T. Hierarchical modularity in human brain functional networks.前面。Neuroinform337 (2009)。
Kennard m a皮层重组运动机能。拱门。神经。精神病学48,227 - 240 (1942)。
贝茨、大肠等。微分单方面病变对语言的影响在儿童和成人生产。大脑的语言79年,223 - 265 (2001)。
安德森,V。,Spencer-Smith, M. & Wood, A. Do children really recover better? Neurobehavioural plasticity after early brain insult.大脑134年,2197 - 2221 (2011)。
以来,t . k .关键时期的监管。为基础。启>。27,549 - 579 (2004)。
Uylings h .发展人类的皮层和“关键”或“敏感”的概念期。语言学习。5659 - 90 (2006)。
Hagmann, p . et al .白质成熟重塑了人类大脑结构连接在后期发展中。Proc。《科学。美国107年,19067 - 19072 (2010)。
Khundrakpam b . s . et al .发育大脑结构网络的组织的变化。Cereb。皮质23,2072 - 2085 (2013)。
公平,d . a . et al。脑功能网络从本地分布式的开发组织。公共科学图书馆Comp。杂志。5e1000381 (2009)。
科尔布,B。,Gibb, R. & van der Kooy, D. Neonatal frontal cortical lesions in rats alter cortical structure and connectivity.大脑Res。645年,85 - 97 (1994)。
寇蒂斯,s . Fromkin V。克拉申,S。Rigler D。,&Rigler, M. The linguistic development of Genie.语言50,528 - 554 (1974)。
Lipska, b . k . &温伯格,d . r .精神分裂症的神经发育模型:新生儿海马体的断开。Neurotox Res。4,469 - 475 (2002)。
Tovar-Moll, f . et al .大脑结构和功能重新澄清保存两半球间的转移在人类生而胼胝体。Proc。《科学。美国188金宝慱官网下载,7843 - 7848 (2014)。
Hagmann, p . et al .映射人类大脑皮层结构的核心。公共科学图书馆杂志。6e159 (2008)。
亲爱的,c . j . et al .预测人类静息状态功能连通性结构连接。Proc。《科学。美国106年,2035 - 2040 (2009)。
确认
自动跟踪,A.Z. and M.B. are supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (grant identifiers: 1050504, 1066779, 1047648 and 1037196) and the Australian Research Council (ID: FT130100589). M.B. acknowledges the support of a Queensland Health Fellowship and the James S. McDonnell Foundation (Brain Network Recovery Group JSMF22002082). The authors thank B. Fulcher for assistance in developing some of the images in this article, and O. Sporns for technical assistance and for generously providing the data used in图3。
作者信息
作者和联系
相应的作者
道德声明
相互竞争的利益
作者声明没有竞争的经济利益。
相关链接
进一步的信息
术语表
- 扩散tractography
-
核磁共振技术大规模重建白质纤维的基础上优惠扩散的水沿着这些纤维的轴。
- 分层模块化
-
的嵌套组织牵一发而动全身的子集,或模块,网络内的节点,这样模块都包含在模块等等,在多个尺度上的组织。
- 图论
-
数学的一个分支关心学习的网络连接元素。通过图论,大脑网络可以被建模为一个节点图(描述单一神经元,神经元的数量或宏观的大脑区域)联系在一起的边缘(描述区域结构或功能的交互)。
- 网络拓扑结构
-
的方式连接的网络组织彼此。
- 功能连通性
-
之间的统计依赖(如相关)神经生理学记录获得从不同的大脑区域。
- 有效的连接
-
一个神经系统产生的因果影响另一个。其测量通常需要的神经动力学模型导致测量神经信号的变化。
- 神经调节
-
神经元活动的监管,提升神经递质系统。
- 度分布
-
在网络节点度值的分布获得。
- 网络碎片化
-
网络分裂成断开连接的节点子集。缺乏这些子集之间的连通性的排除了任何他们之间的通信,即节点不再作为一个集成的系统。
- 结构连接
-
物理连接(即轴突纤维)的大脑区域之间。
- 图案
-
简单,重复出现的模式或子图表示一个更大的网络的构建块。
- Non-stationarity
-
一些时间序列的趋势显示波动在他们的意思是,协方差随着时间的推移和其他描述性的措施。非平稳大脑活动意味着长期时间平均的神经活动可能不会准确地总结动力学在较短的时间尺度。
权利和权限
关于这篇文章
引用这篇文章
Fornito,。,Zalesky,。&Breakspear, M. The connectomics of brain disorders.Nat转速>16,159 - 172 (2015)。https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3901
发表:
发行日期:
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3901
本文引用的
非传统的大脑认知网络参与insulo-Sylvian神经胶质瘤:使用Quicktome病例系列研究和临床经验
中国神经外科杂志(2023)
改变大脑结构和功能连接在大麻用户
科学报告(2023)
内在宏观尺度振荡模式推动远程功能连通性的雌性老鼠的大脑被超速的功能磁共振成像
自然通讯(2023)
试再现性变化多,纵向的大脑网络
科学报告(2023)
白质的异常的拓扑网络甲基苯丙胺依赖患者在基于支持向量机的分类及其应用
科学报告(2023)
